Master Raspberry Pi Remote Monitoring: Free Tools & Tips!
Can a tiny, credit-card-sized computer revolutionize how we monitor and manage systems, both near and far? The Raspberry Pi, with its remarkable versatility and affordability, has become a cornerstone of remote monitoring solutions across a vast spectrum of applications, from home automation to industrial IoT.
The allure of remote monitoring lies in its ability to provide real-time insights and control over devices and systems, regardless of physical location. This capability is increasingly vital in an interconnected world, where the need to manage and maintain complex setups efficiently is paramount. The Raspberry Pi, owing to its compact design, low power consumption, and open-source nature, offers a compelling platform for realizing this vision.
The Raspberry Pi's adaptability shines in diverse scenarios. Consider, for instance, the ability to monitor a fish tank, pool, or even a hydroponics system. By integrating sensors for water quality parameters, such as pH, temperature, and dissolved oxygen, the Raspberry Pi acts as a central hub, displaying real-time data on a connected touchscreen. This empowers users with an unprecedented understanding of their aquatic environments, facilitating timely adjustments and ensuring optimal conditions. Similarly, in industrial settings, the Raspberry Pi can monitor ports, services, CPU load, memory usage, disk usage, and much more, providing critical performance metrics and enabling proactive troubleshooting.
One of the main benefits of using raspberry pi is its versatility, it can be used in various fields. The following table describes the details about the working of raspberry pi in various sectors:
| Application Area | Description | Key Components/Technologies | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Automation | Raspberry Pi serves as a central control unit for smart home systems, managing devices like lights, appliances, and security systems. | GPIO pins, sensors (temperature, motion), Wi-Fi connectivity, home automation software (e.g., Home Assistant). | Remote control, automation of tasks, energy efficiency, enhanced security. |
| Industrial IoT (IIoT) | Monitoring and controlling industrial processes, machinery, and equipment. | Sensors (temperature, pressure, vibration), communication protocols (Modbus, MQTT), industrial-grade Raspberry Pi models. | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, improved efficiency, reduced downtime. |
| Network Monitoring | Tracking network traffic, identifying bottlenecks, and ensuring network performance. | Network monitoring software (Nagios, Zabbix), network interfaces, logging capabilities. | Proactive identification of issues, improved network performance, enhanced security. |
| Environmental Monitoring | Collecting data on environmental conditions such as air quality, weather, and soil moisture. | Sensors (temperature, humidity, air quality), data logging software, internet connectivity. | Environmental awareness, early warning systems, informed decision-making. |
| Smart Agriculture | Monitoring and controlling greenhouse conditions, irrigation systems, and crop health. | Sensors (temperature, humidity, soil moisture), actuators (pumps, fans), control software. | Optimized growing conditions, resource efficiency, increased yields. |
| Vehicle Monitoring | Gathering data on vehicle performance, location, and driving behavior. | GPS module, OBD-II interface, data logging software. | Real-time tracking, performance analysis, improved safety. |
Raspberry Pi's power also extends to renewable energy applications. By installing software like SolarAssistant, users can easily manage and monitor their solar power systems. The Raspberry Pi can communicate with inverters using a USB to RS485 converter, providing valuable insights into energy generation, consumption, and storage. This information can be accessed remotely, empowering users to optimize their solar energy usage and make informed decisions.
For those seeking to manage a fleet of Raspberry Pis or any other Linux device remotely, several tools and methods are available. Securely connecting to remote devices to run tests, deploy updates, or debug applications streamlines development workflows. The remote.it agent, for instance, provides a simple way to establish a secure connection. You can monitor your Pi's system performance from a remote location. Whether you're managing servers, IoT devices, or home automation systems, Raspberry Pi offers an excellent platform for remote monitoring. Several tools and software, like htop and picockpit, are available in the official repository and on GitHub and can be installed to provide additional features/ capabilities.
Remote access is further enhanced by headless installations, where the Raspberry Pi operates without a connected display. For such setups, remote management tools are essential. The Linux dash dashboard, SSH connections, and tools like the 'top' command are valuable for monitoring vital statistics such as CPU load, disk usage, and network information. These tools allow the Raspberry Pi to be monitored over Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or even the internet when combined with a public IP address and appropriate port forwarding. Before you can control your Raspberry Pi from your phone, youll need to enable SSH (secure shell) access. Start by connecting your Raspberry Pi to a monitor and keyboard for initial setup. Navigate to interface options and select SSH to enable it.
A particularly exciting application area is in the realm of drone monitoring. Systems developed to monitor drones via remote IDs can leverage the Raspberry Pi's capabilities. Such systems are designed to be easily extended with additional formats and sniffing types, making them adaptable to evolving drone technologies. Atlas IoT, for instance, uses the Raspberry Pi to create a powerful new monitoring system.
Building a smart home security system using the Raspberry Pi is another compelling project. By harnessing the Pi's GPIO pins, users can interface with sensors, create an affordable and customizable security setup, and monitor their home from anywhere. In the realm of agriculture, the Raspberry Pi can be used as the central control unit for monitoring and adjusting greenhouse conditions. Essential components include sensors for temperature, humidity, soil moisture, and light, as well as actuators for controlling fans, pumps, and lights.
When it comes to software, various options are available for remote monitoring. The "best" choice often depends on the specific needs of the user. Several tools will also work with the old Raspbian operating system, and all of these tools are working with Debian Linux distribution, on which Raspberry Pi operating systems are based.
Getting started with remote.it on Raspberry Pi is straightforward. Download and install the remote.it agent. Start by installing the remote.it agent on your Raspberry Pi. For more accessibility and features attach a Raspberry Pi the the DSE gateway using an Ethernet cable. Download remote window software on the Raspberry Pi to access the full features free of charge. This is the method I have been using on my diesel generators because I can monitor and remotely control them from anywhere in the world.
Setting up a Raspberry Pi for network monitoring involves several steps. Install and configure Nagios on the Raspberry Pi. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create a powerful network monitoring tool using Raspberry Pi.
For those who need to access a Raspberry Pi remotely without a display, a headless installation is ideal. Raspberry Pi OS Lite remote management and access is an important aspect of this. The compact size, low power consumption, and flexibility of Raspberry Pi make it ideal for projects ranging from home automation to industrial IoT applications. Then run the disk imager software and point it to the mounted SD card and the Raspberry Pi OS disk image. Now you can insert the SD card into the Raspberry Pi and then connect it to the micro USB power.
Modern network monitoring demands sophisticated tools, but expensive, with Raspberry Pi you can setup your own system with low cost. Explore 10 exciting Raspberry Pi projects for motor vehicles. One area where the Raspberry Pi is making a difference is in network monitoring. In this article, we discussed the benefits of using Raspberry Pi for network monitoring, setting up Raspberry Pi for network monitoring, installing and configuring Nagios on Raspberry Pi, and tips for effective network monitoring.
The Raspberry Pi's impact extends across diverse fields. Whether its streamlining development workflows, monitoring environmental conditions, or building smart home security systems, the little computer continues to redefine the possibilities of remote monitoring. Its affordability, versatility, and community support make it an invaluable tool for both beginners and advanced users alike.

Remote Into Raspberry Pi From Windows Raspberry
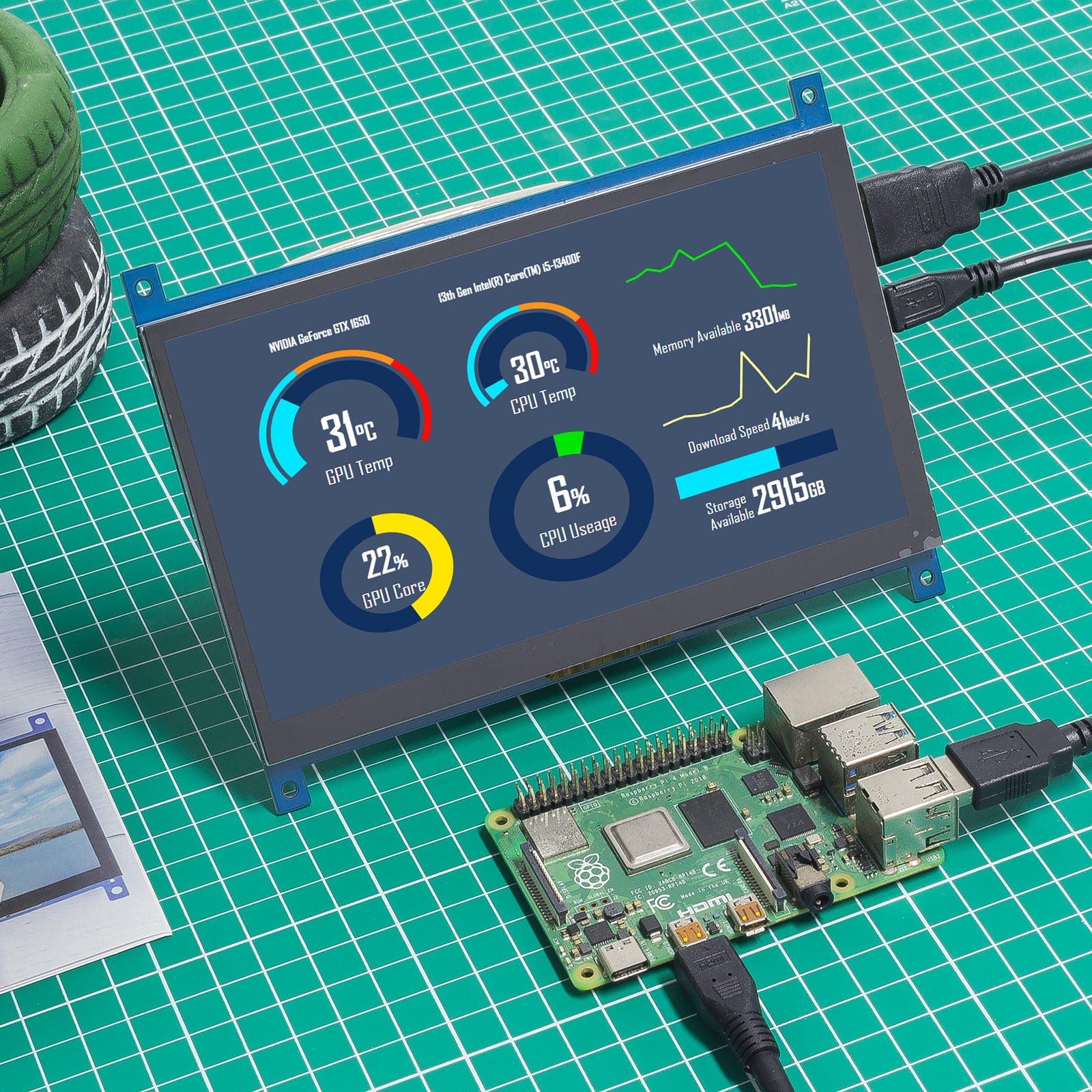
Ultimate Guide Craft A Complete Raspberry Pi System Monitor for PC
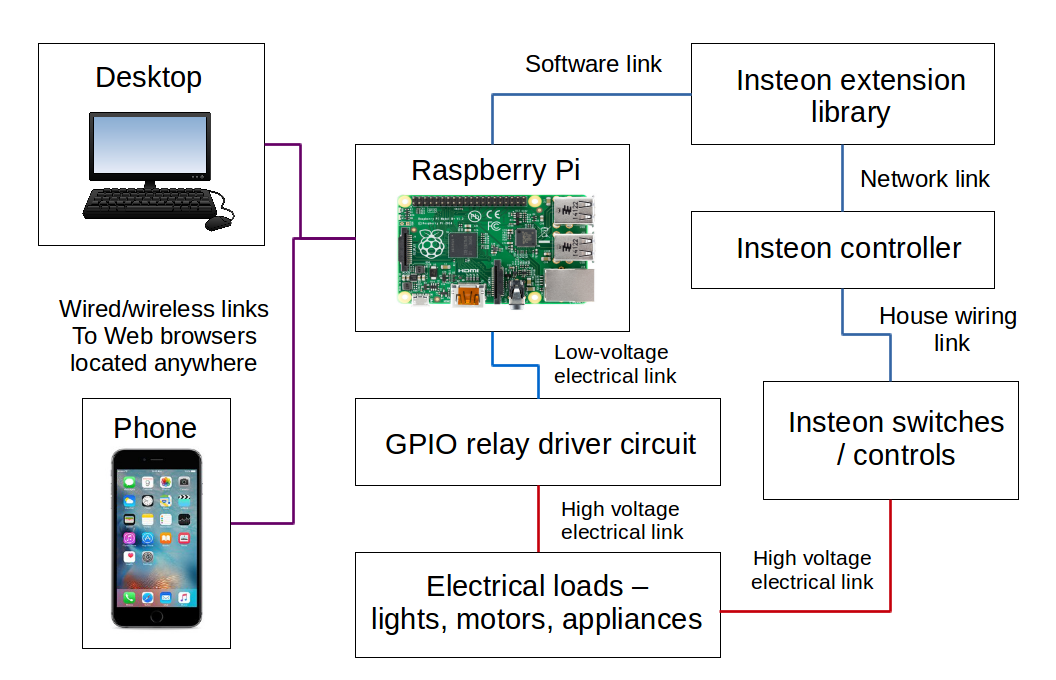
Raspberry Pi Remote Control